Not like it’s title, Logistic Regression is a classification algorithm and never a regression algorithm. Sounds somewhat bizarre proper!. It signifies that the output belongs to a set of finite courses (On this case 2) and the has to foretell it. Let’s have a look at the usual definition.
💡 Logistic regression is a statistical technique used for binary classification issues. Not like linear regression, which is used for predicting steady outcomes, logistic regression is designed to foretell the chance of an occasion belonging to a specific class.
This merely signifies that in logistic regression we predict the chance of an occasion (information level) belonging to a specific class.
Let’s have a look at a easy classification instance for higher understanding:
Now we have a dataset containing the peak and weight (enter options) of canines and cats (output labels) and we now have to coach a mannequin which might predict the species on the premise of the peak and weight of an animal.
Fairly evident from the info itself that usually canines are heavier and taller than cats which sounds about proper. Now, we now have to discover a method to have the ability to calculate the chance of an information level A(top and weight on this case) to belong to both of the courses(species) and Logistic Regression helps up do this.
Word: P(A is a canine) = 1 — P(A is a cat)
For now preserve the above instance in thoughts and allow us to see the way it works by taking an easier instance first after which generalizing it to the above classification drawback.
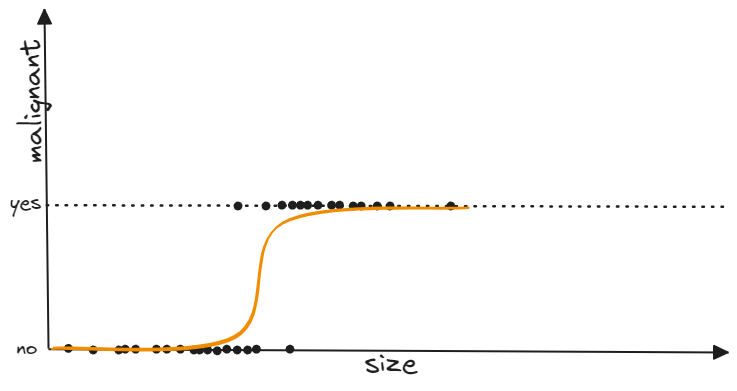
Now we have a most cancers dataset which includes of the scale of the tumor together with the label which tells us whether or not the tumor is malignant(cancerous) or not.
now we are able to attempt to clear up this drawback by becoming a straight line and setting a threshold for the label however this technique doesn’t maintain excellent in case of outliers. Attempt to discover every other motive.
and that’s the place sigmoid operate comes into image.
f(x) = 1/(1 + e^(-x))
Let’s have a look at its graph intently, We wish to be taught a mannequin which inputs a dimension and outputs the character of tumor(say 0 for non-malignant and 1 for malignant. We wish our mannequin to output 0 when the scale of the tumor is much less {that a} specific worth after which return 1 if the scale is bigger than that worth.
To carry out this process of out of the blue altering its worth round a specific threshold and retaining its worth in any other case, logistic regression makes use of a particular operate which is named sigmoid operate.
It’s fairly clear that the worth of the operate is altering rapidly at 0 and is comparatively fixed elsewhere. Additionally by altering the operate f(x) we now have management over the place and steepness of the sigmoid operate. Now allow us to match this operate in our above instance together with some changes within the place and orientation of the operate.
g(ix + j) = 1/(1 + e^-(ix + j))
the place i and j are mannequin parameters and if we regulate them correctly we’ll get a operate which seem like this:
See! this operate appears to suit the info fairly effectively.
However since we would like our mannequin to output the character of the tumor ,i.e., 0 or 1, so we are able to set a threshold worth for the operate say 0.5, that’s, if the worth of the operate is
All the things appears to be good! proper? However how can we do this adjustment and match the operate based on our information.
To get the precise operate we have to have the fixed phrases(i, j) of the operate and to seek out them we use the Price operate of logistic regression.
💡 A value operate, often known as a loss operate or goal operate, is a mathematical measure that quantifies the distinction between the expected values of a mannequin and the precise values of the goal variable. The aim of a price operate is to evaluate how effectively a machine studying mannequin is performing when it comes to its capacity to make correct predictions. The objective throughout coaching is to attenuate this price operate.
The fee operate utilized in Logistic Regression is Binary Cross-entropy.
the place,
N = Whole variety of information factors
yi = floor fact label of the ith datapoint
pi = predicted label of the ith datapoint
Now, allow us to see how efficient is that this price operate with the assistance of some examples.
If the precise label of a datapoint is 0, the loss for various values of the expected labels will look one thing like:
loss = -log(1 - pi)
because of this if the expected worth of label is near zero (nearer to the precise worth) then the loss can also be near zero and if the expected worth of label is shut to 1 then the loss tends to infinity and it is smart, proper!
you your self can see the character of the loss operate if the precise label is 1.
So similar to this we calculate the worth of price operate by calculating loss over the entire information factors and averaging it and as soon as we discover it we are able to simply discover its minima with the assistance of gradient descent.
Gradient descent is a mathematical algorithm which helps us to seek out the minima/maxima of a operate with the assistance of gradients.
We gained’t go any deeper into Gradient descent as it’s nothing completely different from what you may need utilized in every other algorithm and can also be past the scope of this weblog.
#Assuming W and B are outlined and the mannequin is already skilled.
def predict(self, x, threshold):
Z = np.matmul(self.W, X) + self.B
A = sigmoid(Z)
A[A >= threshold] = 1
A[A y_pred = A
return y_pred
Now. Let us get back to our original example.
You must’ve realized the difference between both of the examples, previous example consists of 1 dimensional data(size) whereas the original example has 2 dimensional data(height and weight).
So the
where,
x1 = Weight of the animal.
x2 = Height of the animal.
i, j and k = model parameters.
The cost function still looks the same as there is no change in the dimension of output label, and they are both 1 dimensional.
If we correctly calculate the Cost function values and perform gradient descent properly we should roughly get the following results.
So the model has essentially divided the dataset into 2 areas:
area1 — the area in which the model predicts the animal to be a dog.
area2 — the area in which the model predicts the animal to be a cat.
While there are a few datapoints which are wrongly classified by our model but if it is small enough we are good to go. There are few evaluation metrics for used for classification problems, one of the most common among them is accuracy. Accuracy is the number of data points which are correctly classified by the model divided by the total number of datapoints times 100. basically the percentage of correctly classified data points.
def accuracy(y, y_pred):
y_bool = (y == y_pred)
corr = np.count_nonzero(y_bool)
accuracy = 100*(corr / len(y))
return accuracy
Logistic regression is simple yet powerful classification algorithm which also the basis of neural networks which are capable of learning highly complex patters and hence it is one of the many foundations of deep learning.